Let’s discover together the different types of plastic, but let’s start with the most obvious question, namely what is plastic?
Plastic is an organic material that… but wait, plastic is organic material? Although the adjective ‘organic’ is often associated with living organisms or used as a synonym for natural, in the language of modern chemistry, an organic compound is one formed by one or more carbon atoms through a specific bond (called a covalent bond) to other elements. In particular, plastic is a synthetic organic compound formed by large molecules that appear as particularly long chains, called polymers (from the Greek polýs, meaning “much,” and méros, meaning “part”), in which atoms of other elements besides carbon can be found. Plastic, therefore, is a synthetic organic polymer, created by humans.
The different types of plastic
As we have seen in this article, over time, various types of plastic with unique characteristics have been synthesized. However, the properties of plastics depend not only on the chemical composition of each individual chain but also on the interactions established between the chains and the polymerization process. The most well-known classification of plastics is based on their behavior when heated:
- Thermoplastics, which soften repeatedly when heated and can be welded and easily deformed when hot. Examples include polystyrene, polyethylene, nylon, or Teflon.
- Thermosetting plastics, such as polyurethane or epoxy resin, undergo an irreversible physical change when heated and therefore cannot be melted and reshaped in the recycling process.
It is worth noting that pure plastics are often combined with other substances and additives that can improve or alter some properties, such as color, mechanical strength, rigidity, or resistance to high temperatures.
What are the most common and well-known types of plastic?
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is one of the most common types of plastic and is commonly found in water and beverage bottles or food containers. It is a safe, non-toxic, and durable material, considered valuable for recycling.

- Polyethylene (PE) is a thermoplastic material that is easily colorable and resistant to sunlight. It is produced at different densities for various applications. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is used, for example, to create containers or bottles, caps, etc. PE is also suitable for making bottles but appears opaque and more flexible than PET, which is more transparent and rigid. Expanded polyethylene (EPE) has a low density and a porous structure, making it particularly light and suitable for thermal insulation and packaging.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or vinyl chloride polymer has a wide application in construction, where it is used for the production of fixtures, pipes, vinyl floors, gutters, etc. PVC is very durable and resistant over time.
- Polypropylene (PP) is also used as insulation for electrical cables, replacing PVC, or for the production of pipes. It has properties similar to HDPE, and indeed, PP can be used for the production of containers for food use.
- Polystyrene or styrofoam (PS) is widely used in the construction industry as thermal insulation but is also commonly found as impact protection in packaging.
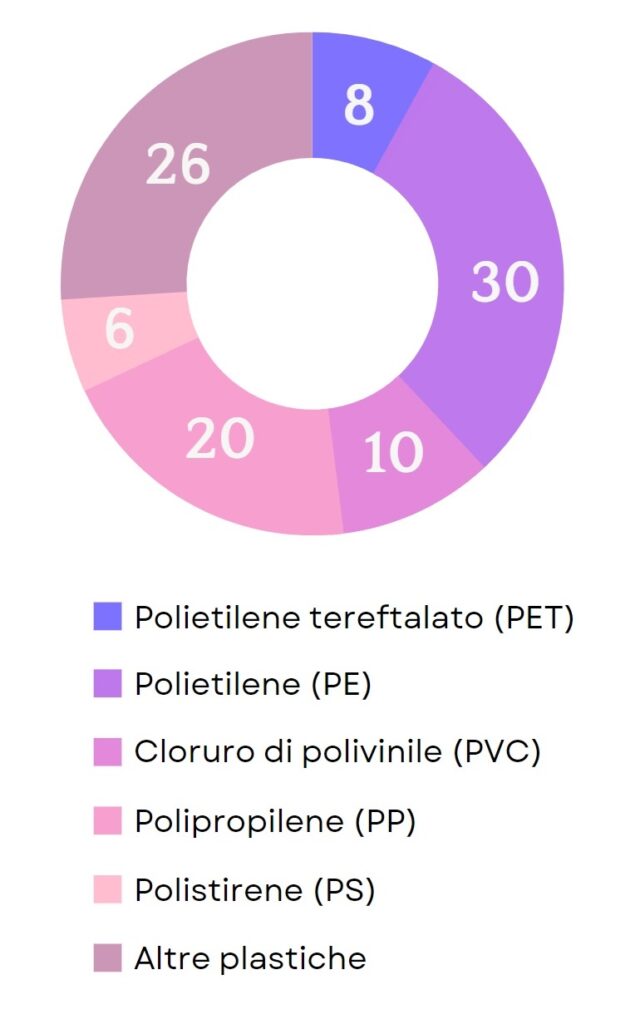
In reality, there are hundreds of types of plastic, but in general, it can be said that thermoplastics are more common than thermosetting plastics, and the five types presented above (PET, PE, PVC, PP, and PS) alone make up almost 75% of the total annual demand for plastic.
What to remember
Plastic is a synthetic organic polymer that can have very different properties depending on its chemical composition and the interactions between the polymer chains that compose it. There are hundreds of different types of plastic, but of these, 5 types are particularly common and constitute over 75% of the annual demand for plastic. These are PET, polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS), all of which are thermoplastic plastics, meaning that they soften when heated and can be easily worked when hot.
More information
More details on types of plastic (in English): here